Recommendation for individuals using a screenreader: please set your punctuation settings to "most."
Descriptive Statements:
- Recognize historic and contemporary theories of atomic structure and the kinetic theory of matter.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the physical and chemical properties of matter.
- Recognize the characteristics of different types of chemical bonds and their effects on the properties of matter.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the organization of the periodic table and its relationship to the structure and behavior of elements.
- Recognize the characteristics of elements, compounds, and mixtures, including solutions, suspensions, and colloids.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the nature of radioactive materials.
Sample Item:
Which of the following is predicted by the kinetic theory of matter?
- The electrons surrounding an atom are in constant motion.
- The pressure of a gas will decrease if its volume is increased.
- The density of a solid depends on its composition.
- The charge of the atomic nucleus depends on its mass.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
B. This question requires the examinee to recognize historic and
contemporary theories of atomic structure and the kinetic theory of matter. According
to the kinetic theory of matter, pressure in a gas-filled container results from
collisions between molecules of gas and the sides of the container. If the volume of a
container is increased, molecules will travel greater distances before striking the
walls, and the collisions will therefore occur less frequently. This will result in
a reduced pressure.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the conservation of matter in chemical reactions and in balancing chemical equations.
- Apply knowledge of chemical formulas, the mole concept, and chemical equations to solve problems.
- Analyze phase changes and the characteristics of the different states of matter.
- Recognize the characteristics of different types of chemical reactions and factors that affect rates of reaction and chemical equilibrium.
Sample Item:
Use the balanced chemical equation below to answer the question that follows.
CaCO3 → CaO + CO2CaCO3 right arrow CaO plus CO2
What is the mass of calcium oxide (CaO) that is produced by heating 80.0 g of calcium carbonate (CaCO3)?
- 44.8 g
- 47.7 g
- 65.9 g
- 70.2 g
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
A. This question requires the examinee to apply knowledge of chemical
formulas, the mole concept, and chemical equations to solve problems. Since the reaction
is already written in balanced form, one mole of CaO is produced for each mole of
CaCO3 that reacts. The molecular weight of CaCO3 is the sum of
the atomic weights of the atoms in CaCO3. The molecular weight of
CaCO3 is 1(40 amu) + 1(12 amu) + 3(16 amu) = 100 amu1 left parenthesis 40 amu right parenthesis plus 1 left parenthesis 12 amu right parenthesis plus 3 left parenthesis 16 amu right parenthesis equals 100 amu. This means that
CaCO3 has a mass of 100 g per mole. Therefore, 80.0 g of CaCO3
represents 0.8 moles of CaCO3 and must produce 0.8 moles of CaO. CaO has
a molecular weight of 1(40 amu) + 1(16 amu) = 56 amu1 left parenthesis 40 amu right parenthesis plus 1 left parenthesis 16 amu right parenthesis equals 56 amu, and 0.8 moles of CaO has a mass
of (0.8) × (56)left parenthesis 0.8 right parenthesis times left parenthesis 56 right parenthesis or 44.8 g.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of the characteristics of different forms of energy and their transformations.
- Apply knowledge of the law of conservation of energy to the analysis of physical and chemical changes.
- Demonstrate knowledge of thermal energy and the transfer of energy through conduction, convection, and radiation.
- Analyze characteristics of electric charge, static electricity, Ohm's law, and series and parallel circuits.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the relationship between magnetism and electricity as well as the properties of permanent magnets.
Sample Item:
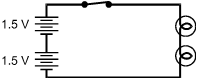
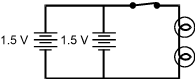
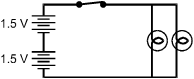
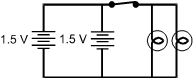
Which of the electric circuits shown below will have the two brightest lights?
Each response is drawn as a closed rectangular circuit with a switch, two 1.5 volt batteries, and two lamps. In each drawing, the switch is on the top side of the rectangle, the batteries are to the left of the switch, and the lamps are to the right of the switch.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
C. This question requires the examinee to analyze characteristics of
Ohm's law and series and parallel circuits. The brightness of an electric lamp is related
to the amount of current through the lamp. Current in a circuit is directly proportional
to voltage and inversely proportional to resistance. The circuits in responses A and C have
a voltage of 3 V since they each have two 1.5 V cells in series. The difference between
these two circuits is that in response A the lamps are in series, and in choice C the lamps
are parallel. Two resistances in series have a greater total resistance than the same two
resistances in parallel.
Descriptive Statements:
- Demonstrate knowledge of Newton's three laws of motion in a variety of situations.
- Solve problems involving force, mass, and motion, including the interpretation of force diagrams.
- Apply knowledge of gravity, friction, pressure, and buoyancy, in a variety of situations.
- Demonstrate knowledge of the principles of work and power, including as applied to simple machines.
Sample Item:
A 10 kg mass is suspended by two cables. In which of the following situations will the
tension in the cable labeled X be the greatest?
Each response shows the 10 kg mass suspended by two cables. In each response, one cable is labeled X, and the angle is dimensioned between each cable and the overhead surface.
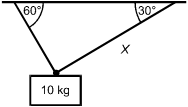
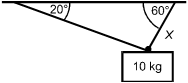
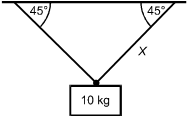
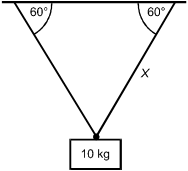
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
B. This question requires the examinee to solve problems involving
force, mass, and motion. In response D, the mass is supported symmetrically by two cables
of equal length. The two cables must share the load equally. In the case in which the
mass is supported by a single vertical cable and hangs straight down (not shown), the
cable would support all of the mass. Response B is closest to this situation and therefore
has the greatest tension.
Descriptive Statements:
- Apply knowledge of the characteristics of mechanical waves and their behavior as they pass through different media.
- Analyze the properties and propagation of sound in a variety of situations.
- Recognize the characteristics of the electromagnetic spectrum.
- Analyze the effects of mirrors, lenses, and prisms on the behavior of light.
- Demonstrate knowledge of refraction and reflection in natural phenomena.
Sample Item:
Sound waves travel at a different speed in warm air than they do in colder air.
Which of the following explains why sound waves travel differently in warm air as
opposed to cold air?
- In warmer air, sound waves travel more rapidly because of the greater kinetic
energy of the air molecules.
- In colder air, sound waves are transmitted more rapidly due to the greater density
of the air.
- In warmer air, sound waves propagate more slowly because they are disrupted by
convection currents.
- In colder air, sound waves are transmitted more slowly due to the higher pressure
of cool air masses.
Correct Response and Explanation (Show Correct ResponseHide Correct Response)
A. This question requires the examinee to analyze the properties and
propagation of sound in a variety of situations. Sound is transmitted as a disturbance
of the medium in which it is traveling. The movement of the sound waves is due, in part,
to the kinetic energy of the molecules of the conducting medium, in this case air. The
molecules in warm air have greater kinetic energy than those in cooler air, and therefore
allow the wave to travel at a greater velocity.

